Bridging Divides: Reducing Conflict in Social Networks
Social networks have become an integral part of our lives, connecting people and facilitating information sharing. However, the growing concerns of polarization and echo chambers within these platforms call for effective solutions. In the research paper "Rebalancing Social Feed to Minimize Polarization and Disagreement," scientists present an innovative algorithm that addresses this issue. By understanding the role of recommender systems and their impact on polarization, this algorithm offers a promising solution to foster more inclusive and constructive online environments.
Understanding Social Networks and Polarization
Social networks are online platforms where individuals interact and share content. The social feed, where users view posts from their friends, plays a crucial role. The frequency at which users see these posts shapes their exposure to different opinions and perspectives. Over time, this exposure can contribute to polarization, where users become more aligned with like-minded individuals and less exposed to diverse viewpoints.
Polarization occurs when users are primarily exposed to content that reinforces their existing beliefs and biases. This leads to the formation of echo chambers, where conflicting viewpoints are suppressed, resulting in increased divisions and reduced understanding between different groups. Recommender systems, which suggest posts based on user preferences, significantly shape content exposure and potentially exacerbate polarization.
Modeling and Frequency Optimization
The research integrates well-established concepts of exposed and innate opinions, distinguishing between what users express online and their underlying beliefs on controversial topics. Beyond simply recognizing these two layers of opinion, the study emphasizes optimizing the frequency with which users encounter the opinions of those they follow.
The proposed algorithm (called LcGD) strikes a balance: it aims to diminish the prominence of polarized opinions while ensuring users still see content that aligns closely with their interests. This approach gradually exposes users to a broader spectrum of opinions, promoting an openness to varied views without overwhelming them.
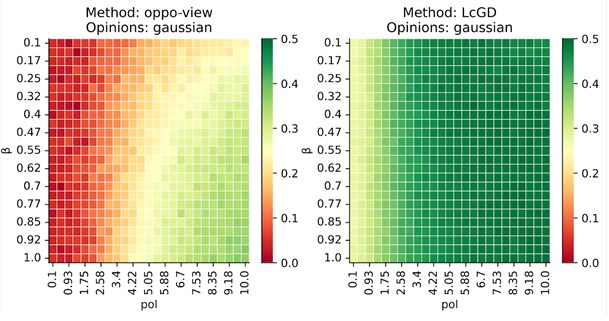
Figure 1. Polarization and disagreement reduction for a baseline (left), the proposed method (right), for different levels of polarization (x-axis), and separation between communities (y-axis).
Implications and Significance
The research paper underscores the importance of addressing polarization and its implications for social networks. By comprehending the connection between the social feed, users' opinions, and the role of recommender systems, the algorithm proposes strategic interventions to reduce the polarization effect and promote exposure to diverse perspectives while preserving users' interests.
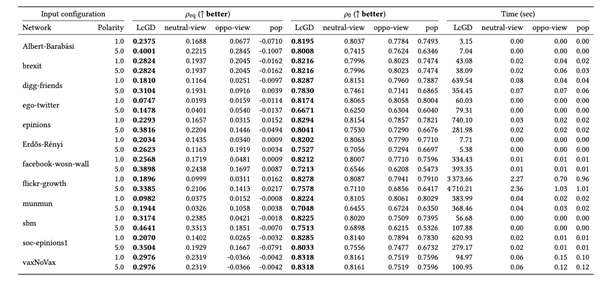
Table 1. Results on reducing polarization and disagreement for directed graphs with Gaussian opinion distribution using a learning rate h = 0.2 and stopping rule d = 10-6|E|.
The algorithm's efficiency is a notable aspect of this research. It demonstrates its effectiveness in large and realistic social networks, making it practical for real-world applications. Leveraging network structure and implementing strategic interventions, the algorithm (LcGD) achieves substantial reductions in polarization levels, surpassing existing recommendation methods that focus exclusively on neutrality, popularity, and diversity (see Table 1). This breakthrough offers promising prospects for creating more balanced and inclusive online spaces.
Reducing polarization within social networks is crucial for fostering understanding, empathy, and constructive dialogue. By actively encouraging exposure to diverse viewpoints, the algorithm helps bridge ideological gaps and promotes meaningful interactions. Its data-driven approach and scalability make it well-suited for application in realistic social networks regardless of the level of polarization or separation between social network communities (see Figure 1).
Conclusion
Addressing the issue of polarization in social networks is increasingly crucial. The research paper "Rebalancing Social Feed to Minimize Polarization and Disagreement" introduces an innovative algorithm that tackles polarization by considering network structure and implementing strategic interventions. With its remarkable efficiency in large and realistic social networks, this algorithm offers a promising solution to foster understanding, reduce conflict, and promote diverse perspectives.
By prioritizing the creation of inclusive and constructive online environments, we can bridge ideological gaps and encourage meaningful dialogue. This research provides valuable insights and tools to mitigate the negative consequences of polarization, allowing social networks to play a more positive role in shaping public discourse and fostering a harmonious online community.
Paper preprint: https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.14486

